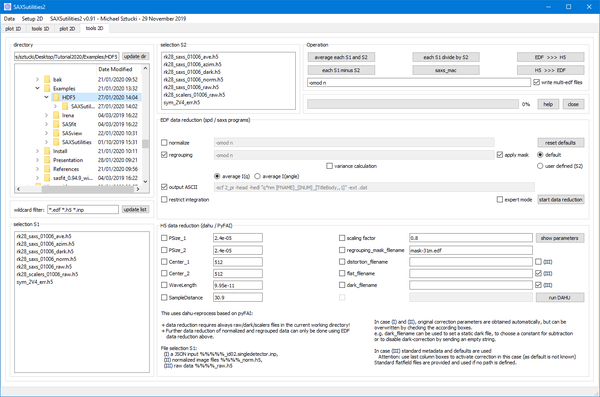
Tools2D
From SAXSutilities wiki
Data reduction of two-dimensional images in HDF5 (Dectris and various ESRF flavours) or EDF format. Routines for data conversion are available.
Contents
Features:
- Conversion from EDF to HDF5
- Conversion from HDF5 to EDF
- NOTE: it is possible to create in this way multi-edf files. It is however currently not foreseen to create multi HDF5 files.
- Averaging, subtraction and division of each two files using saxs programs is foreseen, as well.
Specific Features:
Two different data reduction routines exist:
EDF REDUCTION
- This routine is based on spd / saxs programs.
- Normalization, azimuthal regrouping and output of ASCII files can be selected individually.
- Input format can be EDF or HDF5.
- An approximated variance calculation can be activated.
- The mask information is either taken from a header key ('default') or by a file selection in S2. In any case the mask file must be present in the working directory.
- The integration range can be restricted.
- Incase of problems, error output is available in the (minimized) terminal window of SAXSutilities2.
Typical application: partial azimuthal integration in a reduced angular range
NOTE: This can be also applied to files from the HDF5 REDUCTION pipeline !!
starting from normalized data ('norm')
- Select normalized images in Selection S1.
- Make sure that 'regrouping', 'output ASCII' and 'restrict integration' are all checked.
- Make sure the mask file is present in the working directory. The correct mask file is most of the time determined automatically ('apply mask' checked; 'default' selected).
- Choose if you want to calculate (A) I(q) averaged in a certain angular range or (B) I(angle) averaged in a certain q range.
- In case of (A): specify angular range. Negative angles are possible [-5 , 5]deg.
- In case of (B): specify q range in pixel coordinates (use plot2D with array coordinate system for selection).
- Click 'start data reduction'.
starting from azimuthally regrouped data ('azim' or 'ang')
- Select azimuthally regrouped images in Selection S1.
- Make sure that 'regrouping' is not checked, 'output ASCII' and 'restrict integration' must be checked.
- No mask file is necessary in this case.
- Choose if you want to calculate (A) I(q) averaged in a certain angular range or (B) I(angle) averaged in a certain q range.
- In case of (A): specify angular range. Negative angles are possible [-5 , 5]deg.
- In case of (B): specify q range in pixel coordinates (use plot2D with array coordinate system for selection).
- Click 'start data reduction'.
HDF5 REDUCTION
- This routine is based on dahu / PyFAI
- Data reduction starts always from RAW data. Raw, dark (if applicable) and so called 'scaler' files (metadata!) must be available in the current working directory.
- The only input format is ESRF Lima style HDF5.
- Variance calculation is provided.
- Integration is curently done over the full azimuthal range.
- Data reduction is started by input files containing a JSON string.
Types of input files (for selection S1):
- *_id02.singledetector.inp: File created during experiment.
- *_norm.h5: Reduced data file has history information saved.
- *_raw.h5: Raw data file
In case (1) and (2):
- The original correction parameters can be retrieved automatically and displayed (optionally) by clicking 'show parameters (for first selected file only).
- Parameters can be corrected (i.e. overwritten) by checking one of the available boxes.
- Non-checked values are taken from the input file.
- The name of the file to be reduced is also known from the input file
- Checking either of mask, distortion , flat or dark filename and leaving the field empty, disables the corresponding correction.
- Giving a number for dark_filename, subtracts a constant.
In case (3):
- Metadata are collected from the header (pixel size, center, wavelength distance, scaling factor) and can be overwritten with the static value, if checked.
- The name of the file to be reduced is defined in selection box S1.
- Mask, distortion, flat and dark image names are also taken from the image header, but can be overwritten with a static value (and checking the according box).
- ATTENTION: use the three check boxes marked with (III) to define if you want to do the correction or not.
Typical application of DAHU correction:
You are most probably concerned by case (3).
- Select the Raw images which need to be corrected in selection S1.
- Decide, if you need to correct metadata (e.g. in case you want to correct center coordinates, check the box in front of 'Center_1' and 'Center_2' and provide the correct values; in case you want to update the mask file, put the cross in front of regrouping_mask_filename and provide a filename).
- Decide which corrections need to be done (distortion, flat, dark?) and check accordingly the boxes marked with (III).
- 'run DAHU'.
Make sure that required files (mask, dark images) are available in the specified path (mask) or current working directory (dark).